Using custom image registries in a chaos experiment
A custom container image registry can be defined as a collection of repositories that store container image. It can be either public or private. Few of the container image registries that can be used are Docker, Red Hat Quay, and Google Container Registry among others.
By default LitmusChaos uses DockerHub for managing the different images. These images are then used in Chaos experiments. A few images that are used for the chaos experiments are litmuschaos:k8s, litmuschaos:litmus-checker, etc.
With ChaosCenter, you get the option to use your own custom image registries for Chaos experiments.
Before you begin
To understand the concept of image registry, make sure you are aware of Chaos experiment and the different image registries that are used in it.
Steps to Update Chaos experiment image registry
To updated the chaos experiment image registry, you can go to image registry in ChaosCenter (Project Setup > image registry on the left nav). On clicking the image registry tab, you can see that the default registry server is docker.io, registry name is litmuschaos and it is a public registry.
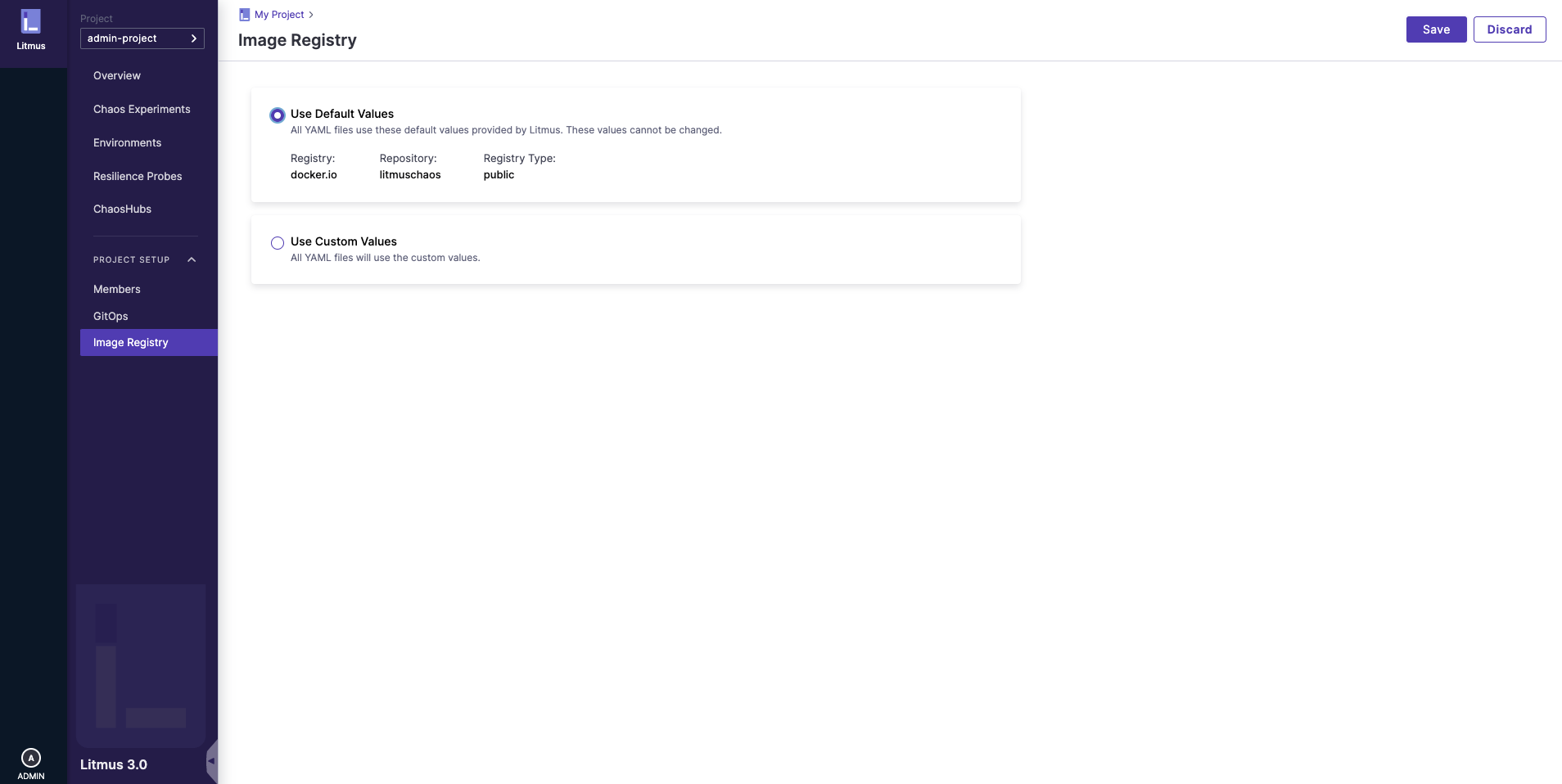
To update this, click on the Use Custom Values option and provide the following details:
- Custom Image Registry (Registry server)
- Custom Repo (Registry name)
- Registry Type (Public/Private)
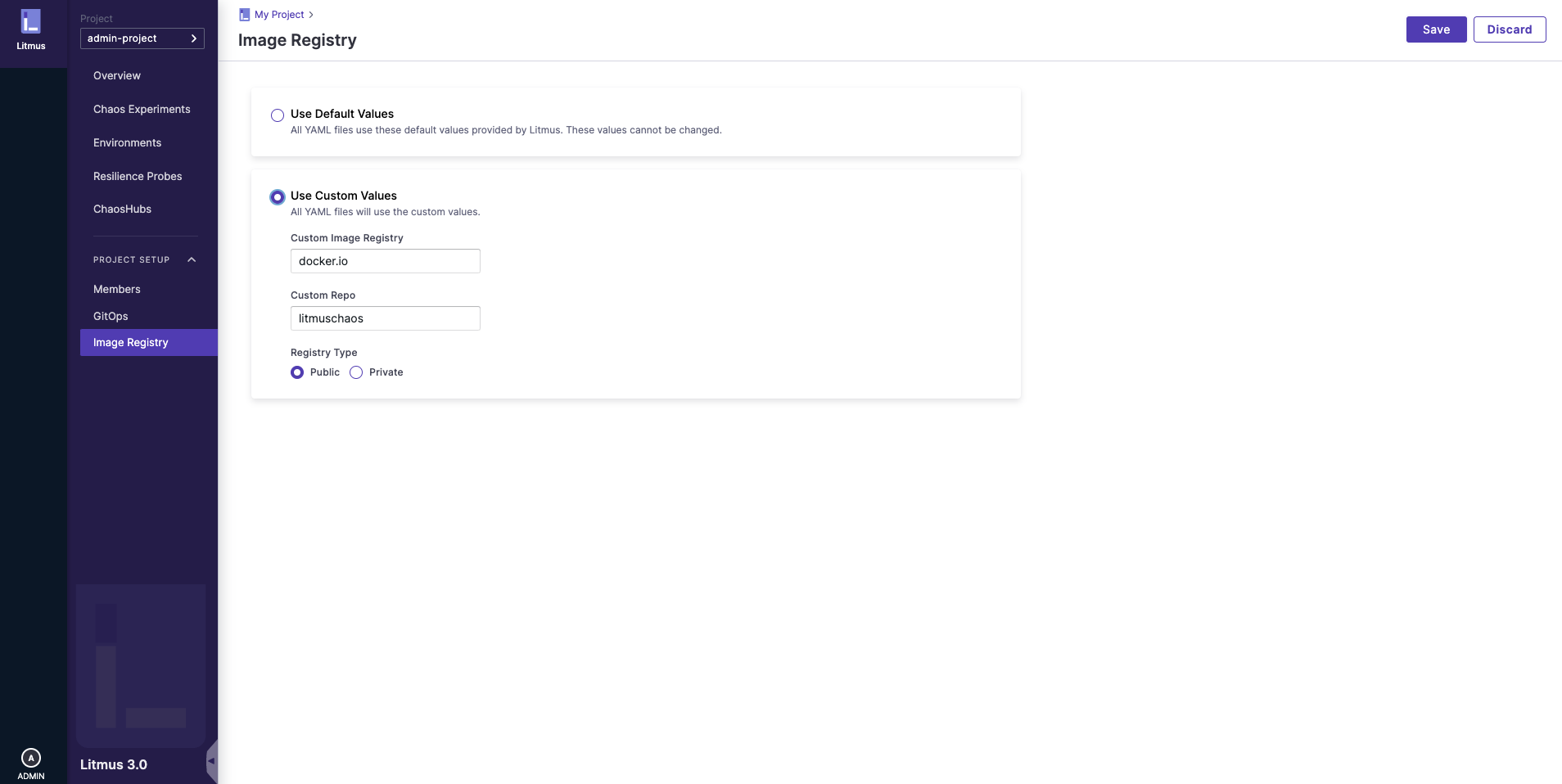
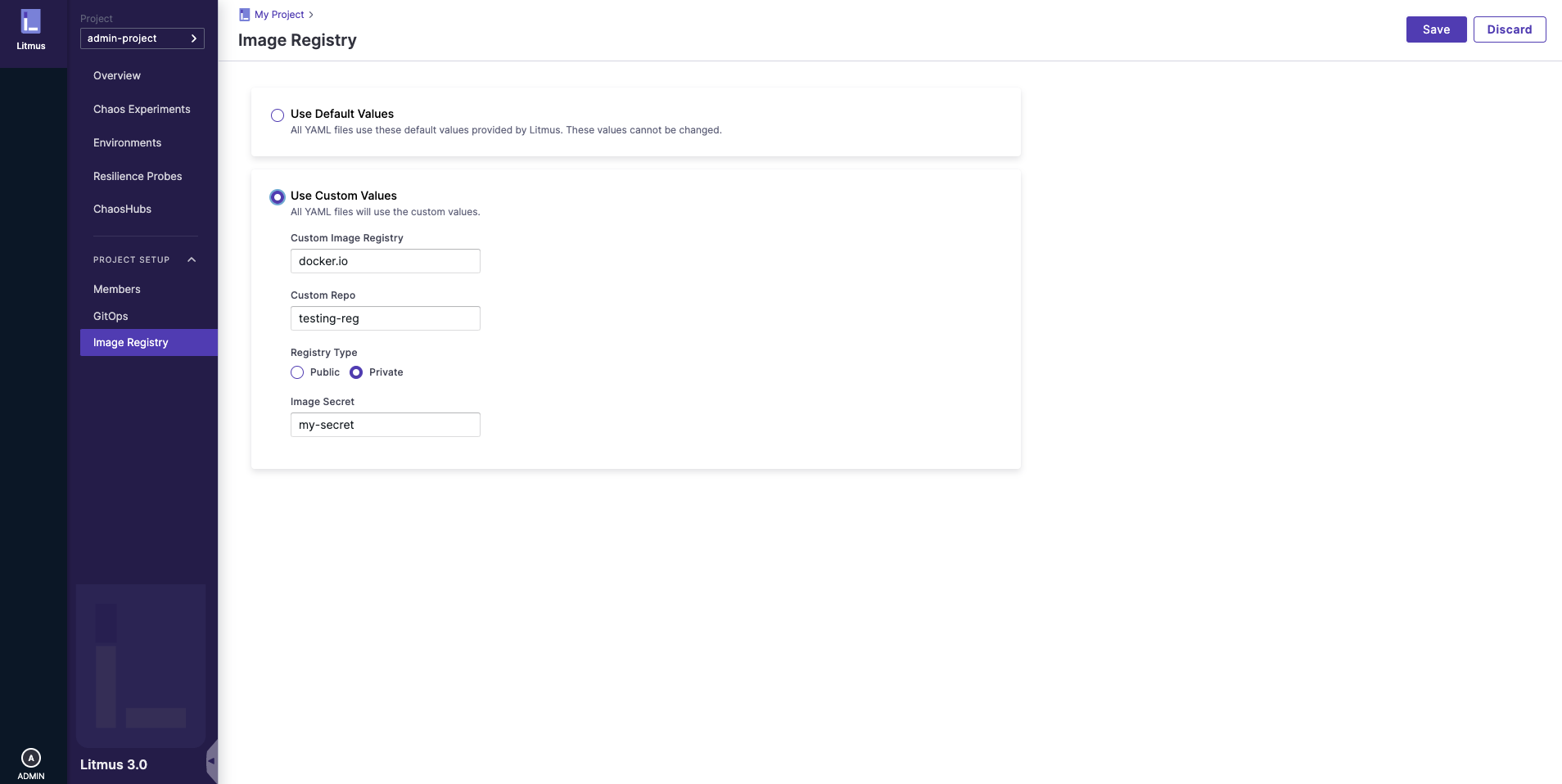
If the registry type is Private, make sure to provide the secret.
Once the details are provided, click on the Save button and you can see the updated image registry changes.
Now, when scheduling a chaos experiment, the image registry changes will be visible. Here's the code snippet from a chaos experiment after the image registry change.
- name: install-application
container:
image: docker.io/testing-reg/litmus-app-deployer:latest
args:
- -namespace=bank
- -typeName=resilient
- -operation=apply
- -timeout=400
- -app=bank-of-anthos
- -scope=cluster
- name: install-chaos-experiments
container:
image: docker.io/testing-reg/k8s:latest